Embarking on a journey to Bam Citadel conjures images of ancient grandeur and mystique. Have you ever wondered who built this architectural masterpiece or pondered over its storied past? Situated in Iran, this ancient citadel is a testament to resilience, especially after its reconstruction after the devastating 2003 earthquake.
In this concise exploration, we delve into everything about Bam Citadel – its origins, the intricacies of its reconstruction, and an aerial view that offers a new perspective on its splendor. This article, presented by MabnaTrip, is more than just a historical account; it’s a gateway to understanding a monumental piece of human heritage. Travel to Iran and arge Bam can be a unique experience for everyone. Join us as we unfold the layers of Bam Citadel’s rich history and enduring legacy.
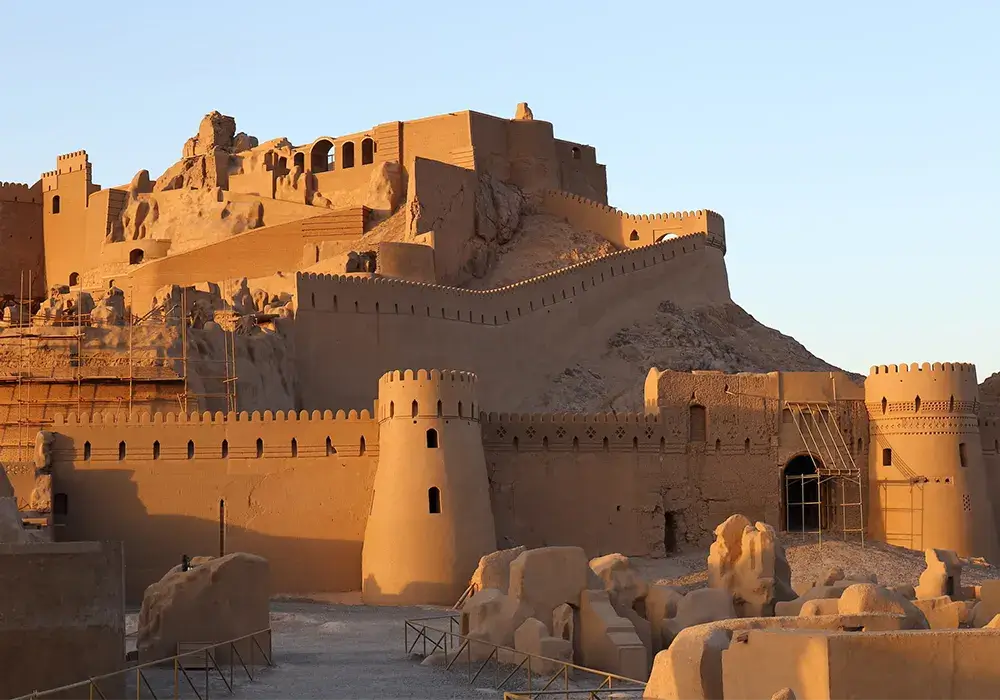

The Historical Evolution of Bam Citadel
The Bam Citadel, or Arg-e Bam in Persian, is an ancient ingenuity and resilience emblem. Its evolution through the centuries is not just a tale of architecture but a narrative woven into the fabric of Iranian history.
Early Origins and Builders: Tracing Back to the Achaemenid Empire
With its imposing adobe structures, Bam Citadel roots back to the Achaemenid Empire, around the 6th to 4th centuries BC. This epoch marks the Citadel’s inception as a fortress and a settlement. Its strategic location in southeastern Iran in map, near Kerman, lent it significance as a military stronghold and a governance center.
Strategic Importance Through Various Dynasties: Parthian, Sassanid, and Safavid Eras
The Citadel saw its significance magnified during the Parthian and Sassanid eras, between 247 BC and the 7th century. It was a vital military base, shielding the empire’s eastern frontiers. The Sassanid period, in particular, was instrumental in the Citadel’s expansion and fortification, reflecting the era’s architectural advancements.
The Safavid period, a period of relative harmony and strength, denoted another part of the Stronghold’s set of experiences. It became a clamoring center point, profiting from its nearness to the Silk Street. This period saw social and financial exercises prospering inside its walls, making it a fundamental piece of the provincial exchange organization.
Can't Find Your Ideal Tour?
Explore Our Customized Tours for a Tailor-Made Experience!
Cultural and Economic Role: Connection to the Silk Road
The Citadel’s proximity to the Silk Road profoundly impacted its development. It became a critical point for trade and cultural exchange between the East and the West. Bam’s thriving silk and cotton industries contributed to its economic prosperity and cultural richness. This period enhanced the Citadel’s architectural complexity by adding residential areas, markets, and public buildings.
Architectural Marvels of Bam Citadel
Bam Citadel, or Arg-e Bam, is a testament to ancient Persian architectural genius. The use of adobe construction not only underlines its historical importance but also its unique adaptation to the desert environment.
Unique Design Features: adobe Construction and Traditional Persian Architecture
The Citadel’s construction primarily involved adobe, made from earth and organic materials, creating a sustainable and resilient structure. This choice of material was essential in the harsh desert climate, providing natural insulation against extreme temperatures. The Citadel’s architecture reflects the ingenuity of ancient builders, who mastered creating robust structures with limited resources. The blend of architectural styles throughout history, from the Achaemenid to the Safavid era, adds to its uniqueness.
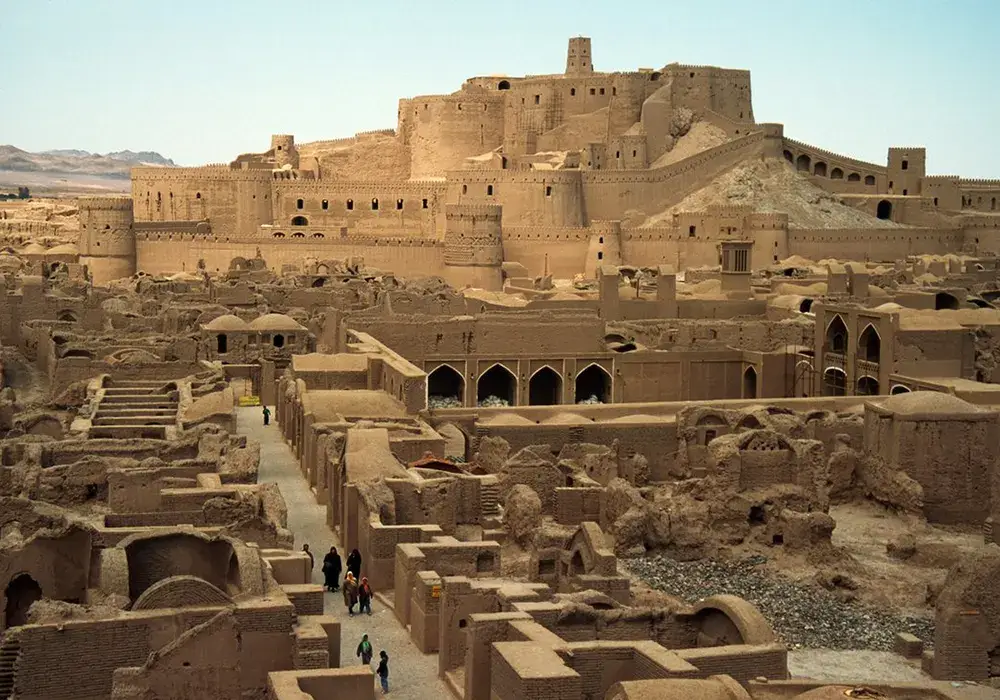

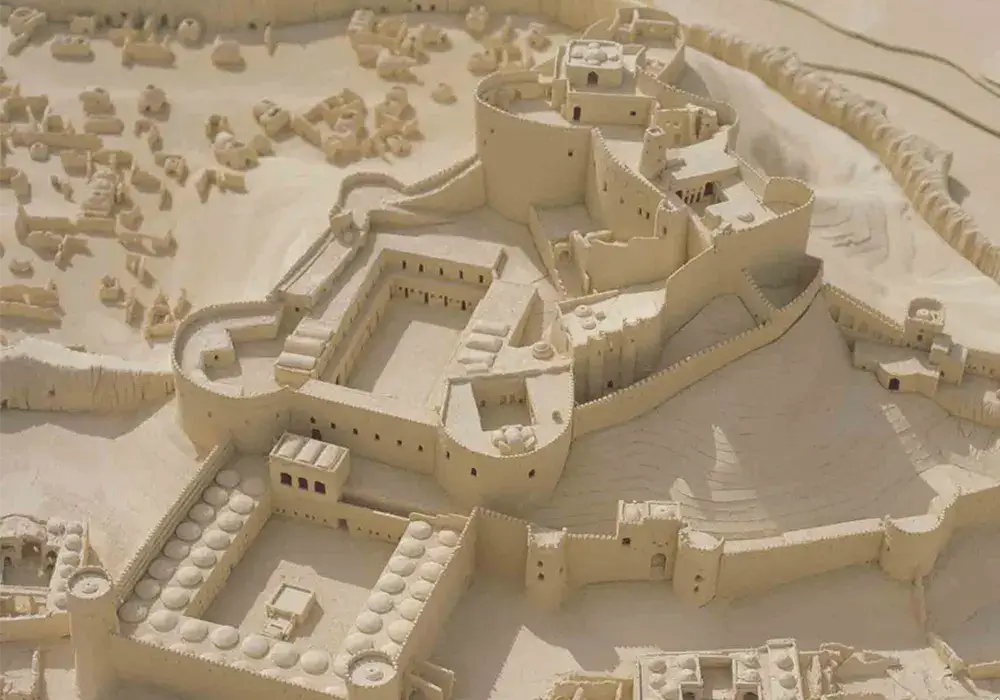
Citadel Layout: Government and Residential Sectors
Bam Citadel was more than just a military stronghold; it was a microcosm of Persian urban design. The Citadel was a self-contained entity divided into two main sectors – the government and the residential sector.
The Government Sector
This sector housed the Citadel’s administrative heart, including fortresses, barracks, and various administrative buildings. Each structure within this sector was strategically placed, serving as a testament to the meticulous planning of ancient architects. The fortresses symbolized strength and protection with their imposing walls and towers. Barracks provided quarters for the soldiers, reflecting the Citadel’s military significance. Administrative buildings were the hub for the Citadel’s governance, showcasing the organizational prowess of its rulers.
Architectural Features of Bam Citadel
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Construction Material | Adobe and mud-brick, suitable for desert climates.
|
Layout | Divided into governmental and residential sectors.
|
Governmental Sector
| Included fortresses, barracks, and administrative buildings. |
Residential Sector
| Featured various types of housing, markets, and public structures.
|
The Residential Sector
The residential sector of Bam Citadel was a bustling area, home to a diverse community. It featured a variety of housing types, catering to different social classes. This sector also included essential public structures like markets, schools, and mosques, which are central to daily life. Markets were vibrant trade centers, showcasing the Citadel’s economic activities. Schools and mosques were educational and religious centers and symbols of the community’s cultural and intellectual life.

Bam Citadel Earthquake
The Bam Citadel, a symbol of Iran’s rich cultural heritage, recently faced its most significant challenge with the catastrophic 2003 earthquake. This devastating event not only shook the physical foundations of the Citadel but also profoundly affected the community and the world’s perception of this historical marvel.
Detailed Account of the 2003 Earthquake: Magnitude, Damage, and Impact
On a pivotal December morning in 2003, the old city of Bam was struck by a tremor at 6.6 on the Richter scale. The earthquake prompted the heartbreaking loss of north of 26,000 residents and left thousands harmed and destitute. The Bastion, Arg-e Bam, experienced broad harm, with around 70% of its construction annihilated. This seismic tremor was not only a catastrophic event but a social misfortune, stripping away hundreds of years of history in simple minutes.
The impact of the earthquake extended beyond the immediate destruction. It raised global awareness about preserving historical sites and implementing better disaster management strategies, especially in regions rich in cultural heritage. The international community responded with support, beginning a challenging yet hopeful journey toward restoration and preservation.
Bam Citadel Earthquake – Before and After Comparison
The Reconstruction of Bam Citadel
The restoration of Bam Citadel after the catastrophic 2003 earthquake is not just a tale of rebuilding ancient walls; it’s a narrative of resilience, innovation, and global collaboration. This section will explore how this iconic heritage site rose from the ruins, weaving together the traditional with the modern and bringing together an international community in its revival.
Overview of the Restoration Process: Phases, Challenges, and Achievements
The reconstruction of Bam Citadel has been a journey marked by numerous phases, each presenting its challenges and achievements. Initially, the focus was on clearing the rubble and salvaging whatever historical elements could be preserved. This phase was crucial in setting the foundation for subsequent reconstruction efforts.
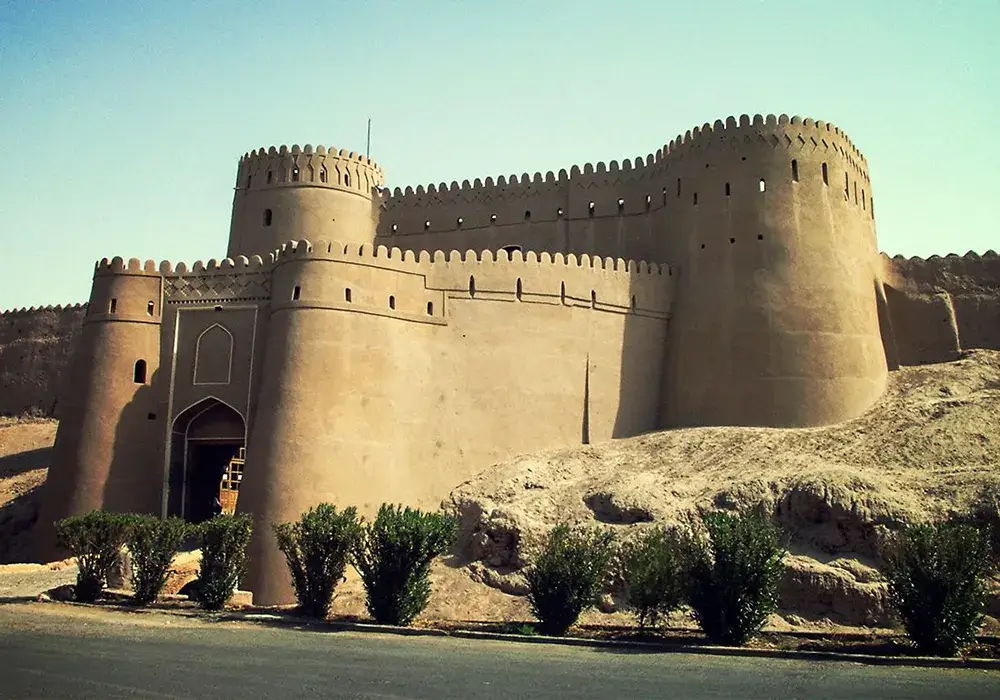

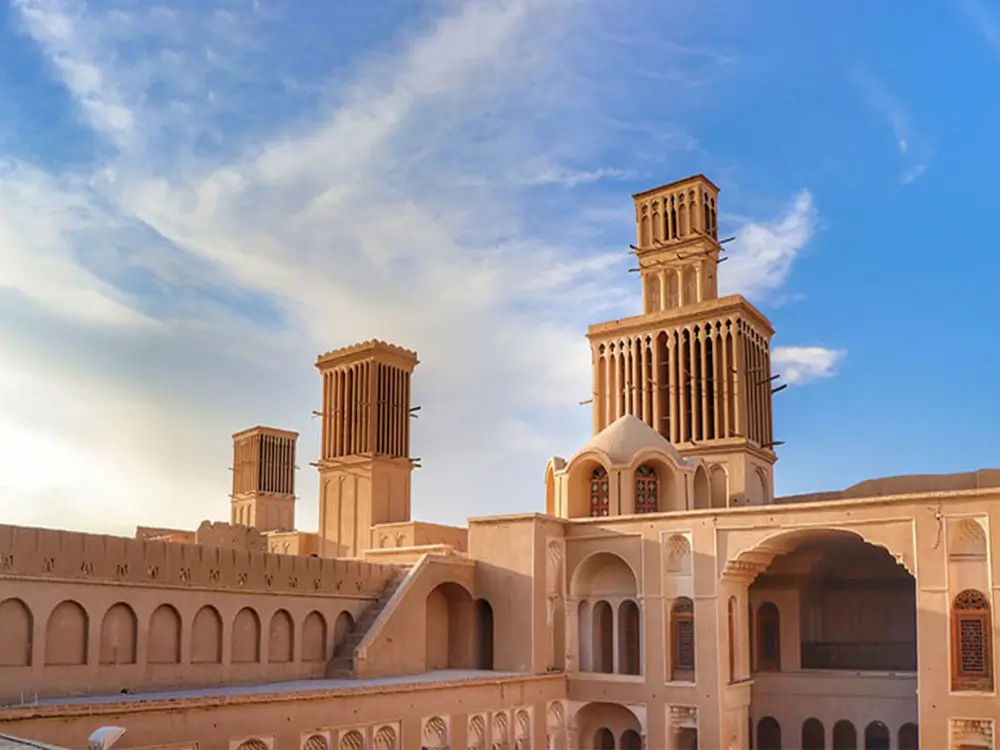
Bam Citadel Today, Best place to Visit in Iran
Bam Citadel, a historical marvel in southeastern Iran, stands today as a testament to resilience and cultural heritage.
Visitors to Bam Citadel today are greeted by an awe-inspiring sight. The ancient walls, towers, and structures, painstakingly rebuilt, offer a window into Iran’s rich history. The Citadel’s adobe architecture, characteristic of old Persian construction, has been preserved, retaining its original charm and authenticity. The site now showcases a blend of actual structures and carefully executed reconstructions.
As you walk through the Citadel’s alleys, you can feel the pulse of history in its restored bazaars, homes, and public spaces. Each corner tells a story of a bygone era, brought back to life through meticulous restoration efforts. The Citadel, previously a victim of time and natural disasters, now stands proudly, inviting visitors to explore its depths and discover the secrets of its past.
Impact of Restoration Efforts on the Site’s Appearance and Tourism
The restoration of Bam Citadel was not just about rebuilding physical structures; it was about reviving a cultural symbol. The efforts involved international collaboration, with experts from around the globe contributing to its reconstruction. This global initiative restored the Citadel’s physical beauty and status as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, attracting worldwide attention and interest from history enthusiasts.
Post-restoration, Bam Citadel has witnessed a significant increase in tourism. Visitors are drawn to its unique architectural style and the story of its revival. The site now offers guided tours, providing insights into its history and the reconstruction process. Educational programs and cultural events have become a regular part of the Citadel’s offerings, further enhancing its appeal as a tourist destination.
Bam Citadel’s Restoration Timeline
Bam Construction: Techniques and Innovations
The construction of Bam Citadel, a historical marvel in Kerman, Iran, is an exemplary blend of ancient techniques and modern adaptations, mirroring a journey through time and innovation. This article delves into the traditional building methods that shaped the original structure of Bam Citadel and the contemporary approaches adopted to reinforce its resilience and sustainability, especially after the devastating 2003 earthquake. If you are interested in Kerman Tour, you could get a free consultation now!
Ancient Building Methods: Adobe and Mud-brick Techniques
Bam Citadel, locally known as Arg-e Bam, is renowned for using adobe and mud-brick, traditional building materials used in the ancient city for centuries. These materials are a testament to the ingenuity of ancient Persian architects and an integral part of Iran’s cultural landscapes. The adobe construction, characterized by sun-dried bricks made of earth, water, and organic materials like straw, offers a unique aesthetic synonymous with ancient Persian architecture.
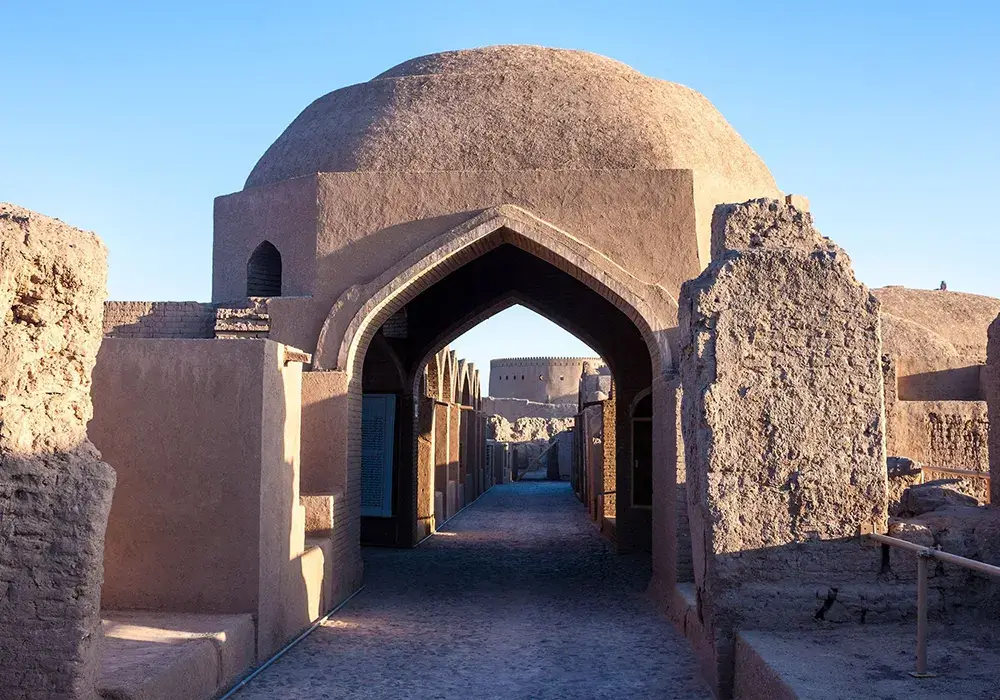

Traditional Techniques of Bam Citadel
- Adobe Construction: Utilizing locally sourced earth and straw shaped into sun-dried bricks.
- Mud-brick Masonry: An age-old technique emphasizing natural insulation and compatibility with the Kerman Iran Bam desert climate.
Modern Adaptations: Integrating Seismic Resilience and Sustainability
Significant efforts have been made to reconstruct and preserve the Bam Citadel in the wake of the Bam earthquake. Modern engineering practices are being integrated with traditional methods to enhance the structure’s seismic resilience, ensuring the longevity of this world heritage site. Sustainable practices are also being employed, using eco-friendly materials and techniques that align with the Citadel’s original aesthetic and functional aspects.
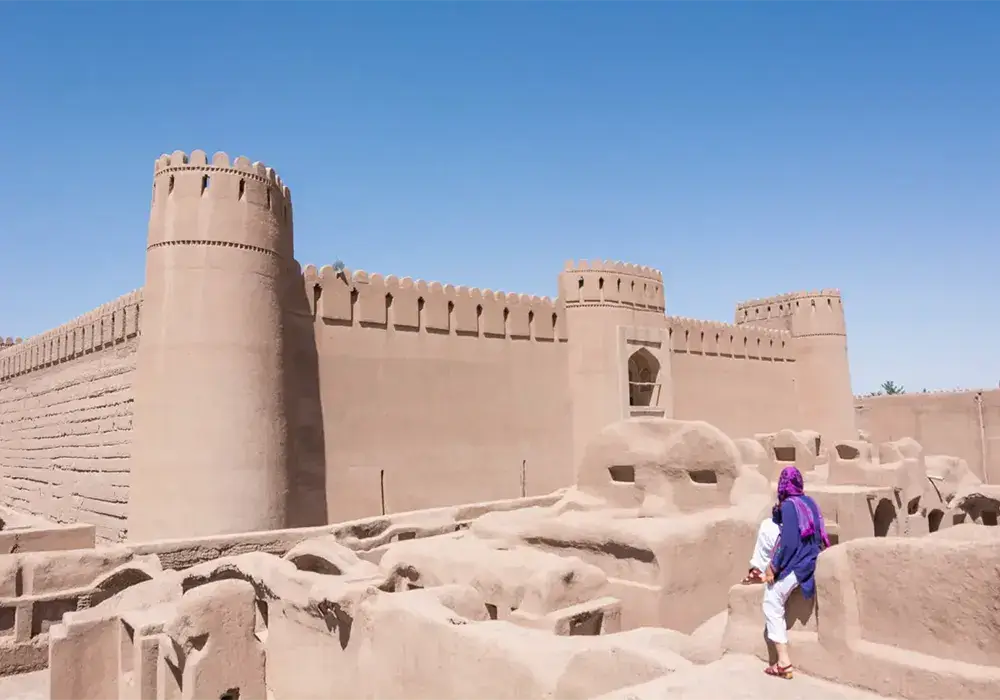

Innovations in Reconstruction
- Seismic Resilience: Incorporating modern engineering solutions to strengthen structures against future earthquakes.
- Sustainable Practices: Utilizing environmentally friendly materials and methods to preserve the Citadel’s authenticity.
Visitor Guide to Bam Citadel
Bam Citadel, a historical marvel in the Kerman region of Iran, is a testament to ancient architecture and a beacon for tourists worldwide. This guide aims to provide practical information for those planning to visit this UNESCO World Heritage site, famously known as Arg-e Bam. We will discuss the best times to visit, accommodation options, local cuisine, and tips for a meaningful experience, ensuring that your visit to this ancient citadel is enjoyable and culturally enriching.
Practical Information: Best Times to Visit, Accommodations, and Local Cuisine
Best Times to Visit
- Ideal Months: To avoid the intense summer heat, the best time to visit Bam Citadel is from late autumn to early spring, particularly between October and April.
- Festivals: Keep an eye on local festivals such as Nowruz, which offer a unique cultural experience.
Accommodations
- Local Stays: There are various accommodation options in Kerman Iran Bam, ranging from traditional guest houses to modern hotels.
- Book in Advance: During peak seasons, booking your stay well in advance is advisable.
Local Cuisine
- Culinary Delights: Don’t miss out on the local cuisine, which includes traditional dishes like ‘Kermani Pomegranate Stew’ and ‘Bam Dates.’
- Food Tours: Join local food tours to experience a variety of tastes and flavors.
Tips for a Meaningful Visit: Cultural Etiquette and Must-See Attractions
Cultural Etiquette
- Respect Local Customs: Be mindful of the cultural norms, such as dressing modestly and showing respect in religious places.
- Interaction with Locals: Engage with locals respectfully to understand their world heritage and the impact of the 2003 earthquake.
Must-See Attractions
- Adobe Structures: Explore the unique adobe architecture, Bam Citadel’s construction hallmark.
- Citadel’s High Point: Visit the highest point of the citadel for a panoramic view of the ancient city and surrounding cultural landscapes.
All the Best Destinations for Tourism in Bam, Kerman
In addition to the Bam Citadel, several other attractions in and around Bam are worth visiting:
- Arg-e Bam: The largest adobe building in the world, this citadel is a must-see for its historical significance and architectural beauty.
- Deh Bekri: This village, situated in the skirts of Sheer Mountain, is known for its natural beauty and modern villas, making it a popular summer retreat.
- Fahraj Village: Noted for its ancient ruins and traditional handicrafts, this village offers a peek into the region’s rural lifestyle and cultural heritage.
- Hezar Mountain: Ideal for hiking and nature enthusiasts, this mountain provides stunning views and a refreshing escape from the arid climate of Bam.
- Cultural and Handicraft Experiences: Engage in local arts and crafts, including textile weaving, which gives insight into the region’s artistic traditions.

Time of Visit and Prices
The best time to visit Bam and its surrounding attractions is October to April. During these months, the weather is milder, making it more comfortable for sightseeing and exploration. The Bam Citadel, open year-round, charges a nominal entry fee, offering visitors a budget-friendly opportunity to delve into Iran’s history.
Visiting Fahraj Village and Hezar Mountain is generally accessible, though there might be small charges for accessing certain areas or services. It’s always a good idea to check for the latest information on timings and prices before planning a visit.
Accommodation in Bam ranges from budget-friendly guesthouses to more luxurious options, catering to various preferences and budgets. Local dining experiences are also affordable, allowing tourists to enjoy traditional Iranian cuisine without stretching their budgets.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of the Bam Citadel, a symbol of endurance and architectural marvel, we’ve journeyed through its storied past, from its ancient origins to its remarkable reconstruction after the 2003 earthquake. This ancient city and world heritage site, with its adobe structures and cultural landscapes, stands not just as a testament to Iran’s rich history, particularly in Kerman, but as a beacon of resilience. Our insights into the citadel’s restoration, blending traditional techniques with modern adaptations, highlight a thoughtful balance between preserving history and embracing progress.
MabnaTrip invites you to delve further into the wonders of Bam and beyond. Discover more stories and insights that await in our collection of blog posts, where each narrative brings you closer to the heart of diverse cultures and incredible destinations. Let the Bam Citadel be just the start of your journey into the depths of history and beauty.